Deployment
Deployment process
After developing the model or converting the plaintext model into an FHE model, deploy it using Aegis's client and server features. In a typical Aegis deployment:
-
The server holds the artifacts generated by Aegis after compilation, specifically the server.zip file, which includes the program specification and FHE binary files (*.so).
-
The client holds the artifacts generated by Aegis after compilation, specifically the client.zip file, which includes the program specification.
The complete process is shown in the figure below:
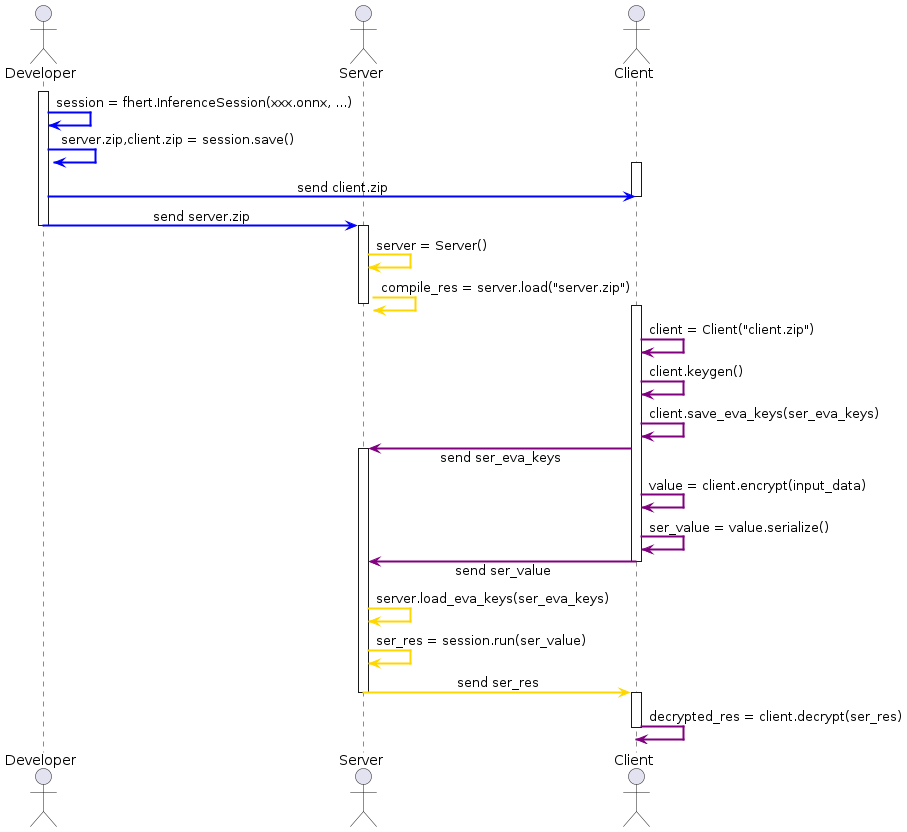
Step-by-Step Deployment Guide
Follow these steps to develop, deploy, and use your privacy-preserving model.
-
Develop and compile the model (developer-side)
You can use the techniques discussed in the previous chapters to write your own model or reuse pre-trained models. The following code uses a pre-trained model.
from primus.aegis.fheruntime import FHEInferenceSession as InferenceSession
session = InferenceSession("/path/to/add_model.onnx")The InferenceSession(...) function compiles the ONNX model and creates a session object to associate the compilation results.
-
Save deployment files (developer-side)
After compiling the model, save the required files for service deployment.
server_zip, client_zip = session.save()The server_zip contains the program_spec.json and *.so files. The client_zip contains the program_spec.json.
The program_spec.json includes security parameters for generating the keyset, model input/output information, and other global configuration details. The *.so file is the compiled model binary.
After compilation completes, distribute the server.zip artifacts to the server and client.zip to client devices for deployment.
-
Load server.zip(server-side)
The server creates a service object using the server.zip file provided by the developer.
server = Server()
server = erver.load(server_zip) -
Create client object (client-side)
After receiving the client_zip file sent by the developer-side, create a client object.
client = Client(client_zip) -
Generate the keyset (client-side)
After completing the client object creation, perform key generation. The FHE CKKS scheme will generate the Private key, Galois keys, relinearization keys, and public key.
client.keygen() -
Serialize the public key, Galois keys, and relinearization keys (client-side)
eva_keys = "/tmp/eva_keys.bin"
client.save_eva_keys(eva_keys) -
Send the serialized public key, Galois keys, and relinearization keys to the server (client-side)
-
Encrypt the input data (client-side)
ser_enc_val1, ser_enc_val2 = client.encrypt([12.5, 76.3]) -
Send the serialized encrypted data to the server (client-side)
-
Deserialize the public key, Galois keys, and relinearization keys (server-side)
server.load_eva_keys(eva_keys) -
Perform the computation and serialize the computation results (server-side)
ser_enc_output = server.run([enc_val1, enc_val2]) -
Send the serialized computation results to the client (server-side)
-
Deserialize the computation results and decrypt the computation results (client-side)
pt_output = client.decrypt(ser_enc_output)